使用UART
接收数据
自串口端口进来的数据将保存在接收缓存区。 在此接收缓存区保存的值通过pid_read函数读取来接收数据。
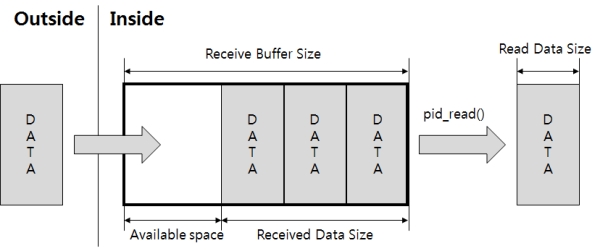
pid_read函数如下使用。
pid_read($pid, $var[, $len]);$var是要保存读取数据值的变量,$len代表可以读的字节数。
例
此例约每一秒确认自UART接收的数据并输出。
$pid = pid_open("/mmap/uart0"); // open UART 0
pid_ioctl($pid, "set baud 9600"); // baud rate: 9600bps
pid_ioctl($pid, "set parity 0"); // parity: none
pid_ioctl($pid, "set data 8"); // data bit: 8
pid_ioctl($pid, "set stop 1"); // stop bit: 1
$rxbuf = pid_ioctl($pid, "get rxbuf"); // get size of receive buffer
while(1)
{
$rdata = "";
$len_tot = pid_ioctl($pid, "get count rx"); // get total size of data received
$rxlen = pid_ioctl($pid, "get rxlen"); // get size of data received
$rx_free = $rxbuf - $rxlen; // get remaining size
echo "$rx_free / $rxbuf\r\n"; // print remaining size
$len = pid_read($pid, $rdata, $rxlen); // read data
echo "len[total] = $len[$len_tot] / "; // print size of read data
echo "rdata = $rdata\r\n"; // print read data
sleep(1);
}
pid_close($pid);发送数据
利用pid_write函数写入的数据保存在发送缓冲区,通过UART向外部传送。
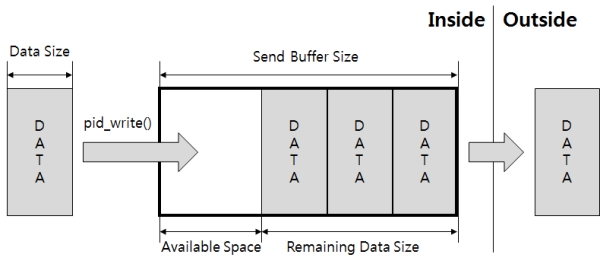
如下使用pid_write函数。
pid_write($pid, $var[, $wlen]);$var是保存要使用的数据的变量,$wlen是要使用的字节数。
例
此例子每一秒确认发送缓冲区的剩余空间通过UART输出数据。
$len_tot = 0;
$sdata = "0123456789";
$pid = pid_open("/mmap/uart0"); // open UART 0
pid_ioctl($pid, "set baud 9600"); // baud rate: 9600bps
$txbuf = pid_ioctl($pid, "get txbuf"); // get size of send buffer
while(1)
{
$len_tot = pid_ioctl($pid, "get count tx"); // get total size of transmitted data
$txfree = pid_ioctl($pid, "get txfree"); // get remaining size
echo "txfree = $txfree\r\n"; // print remaining size
$len = pid_write($pid, $sdata, $txfree); // write data
echo "len[total] = $len[$len_tot]\r\n"; // print length of data sent
sleep(1);
}
pid_close($pid);在上面的代码中pid_write函数的第三个参数是写入数据的长度。 为了避免丢失数据,写入数据长度应小于发送缓冲区的剩余空间大小。 因此建议确定缓冲区的空间后设定其以下的值来设定写入数据长度。